《關於我怎麼把一年內學到的新手 IT/SRE 濃縮到 30 天筆記這檔事》 Day 10 Kubernetes - Storage & ConfigMap & Secret
本篇大綱
這篇將會介紹在 K8s 組出服務必備的第三元素:Storage & ConfigMap & Secret。
內文
K8s 另一個很重要的東西就是儲存了,Docker 可以用 --volume 直接連結好位置就可以永久儲存,可是 K8s 他無法像 Docker 那麼方便,他會需要 Persistent Volume & Persistent Volume Claim 來完成。
設定檔通常都是小檔案,放在 Persistent Volume 是有點大材小用,因此就會有 ConfigMap 解決這情境,那如果有些參數是不能直接在 K8s YAML 檔案上面,那該怎麼辦?Secret 就是好用的東西,那我就來一個個介紹吧!
Persistent Volume
Persistent Volume 簡稱 PV,你可以把他想像成硬碟,建立好幾組硬碟,硬碟也有分好幾種方式:
- AWS, Azure, GCP(這種公有雲都有相對應的 Solution,這邊只會提私有雲常用的策略)
- CephFS, RBD
- GlusterFS
- OpenStack Cinder CSI(後面有一篇會寫到如何跟 OpenStack 整合)
- HostPath(官方有說明 Production 避免使用它,容易產生系統漏洞)
- iSCSI
- local(掛在 Node 的硬碟上儲存)
- NFS
這裡會給予 NFS 的範例,但是 Demo 的時候不會有 NFS,因為我們沒有 NFS Server。
1 | |
.spec.capacity.storage 就是儲存空間大小
.spec.accessModes[] 就是這個 PV 能給 Node 掛載模式,這裡不是在指 Pod 喔!
能跟 OpenStack 整合的就 Cinder CSI,後面有篇文章會說如何讓 OpenStack 跟 PVC 動態串接。
Persistent Volume Claim
Persistent Volume Claim 簡稱 PVC (這裡的 PVC 不是聚氯乙烯),它就是要負責去提出要占用哪一顆硬碟 (Persistent Volume),根據它的需求去拿取。
1 | |
PVC 只要看到有符合需求的 PV 就會顯示 Bound,代表綁定成功,但如果像現在這樣情況,需求要 20Gi,但是 PV 只有 1Mi,那他們之間就不會有綁定。
明天文章的 Demo 是不會有 PV & PVC,空間都會使用 emptydir,也就是臨時用的資料夾,emptydir 的特性就是只要 Pod 在節點上被刪除,資料就會遺失,這個要注意。
ConfigMap
顧名思義,通常會把設定檔放在 ConfigMap,可以用兩種方式 file 或 env 型態
那我使用 nginx.conf 作為示範 file:
1 | |
把他儲存以後
1 | |
把它 Describe 一下:
1 | |
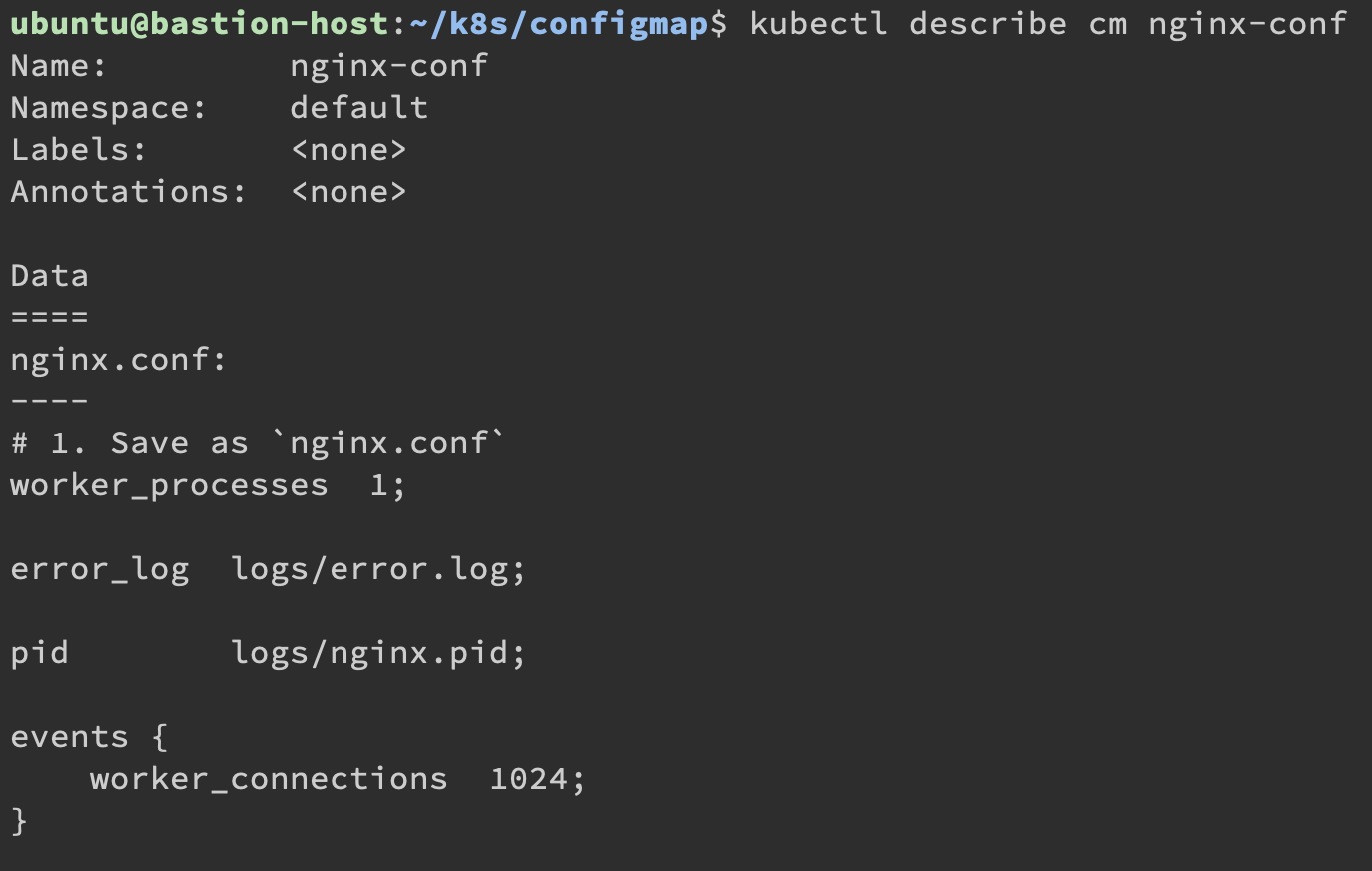
這樣顯示就代表設定檔有進去了。
1 | |
那我們就來 apply 進去:
1 | |
最後把 Pod 的 log 結果印出來:
1 | |
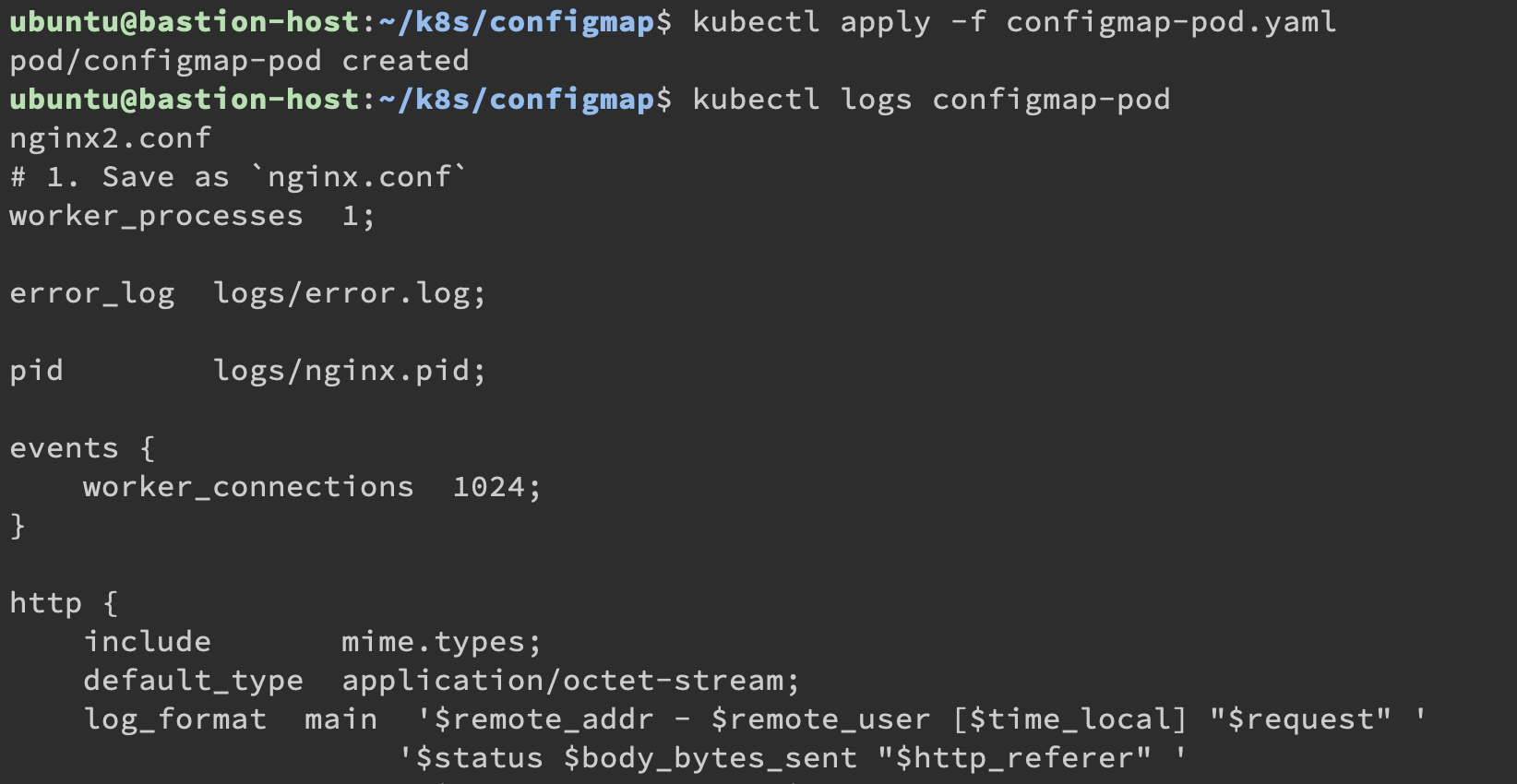
這個是把 ConfigMap 當作 Volume 去傳進 Pod 裡面,想要當作 env 參數可以去參考官方範例,這裡因為篇幅限制就讓各位知道概念。
記得把 nginx-conf ConfigMap 刪掉:
1 | |
Secret
Secret 都會放的是機密類的資料,只要有像是資料庫的初始產生密碼,或者公鑰私鑰,這些都不適合直接暴露在文件中都算機密類。
Secret 提供了 8 種儲存方式:
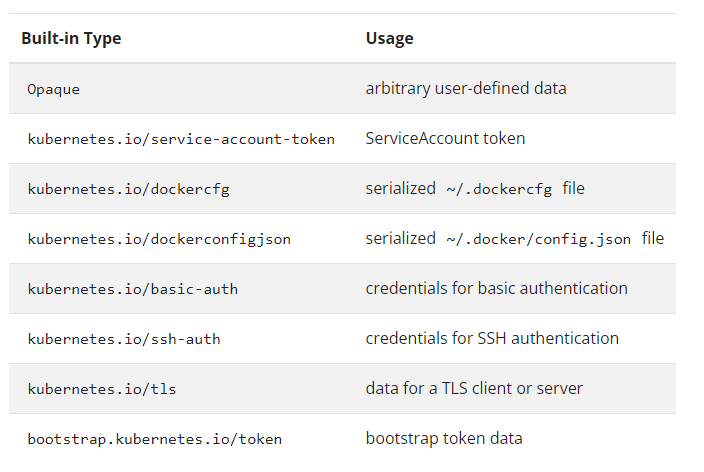
我實際上比較常使用的是 Opaque 跟 kubernetes.io/tls。
除了上面有所說的特殊用途以外,通常都是使用 Opaque 的型態。
Opaque 是這樣建立出來:
1 | |
對,你有沒有發現,其實這跟 ConfigMap 差不多,差異是把 configmap 換成 secret generic 而已。
那我們來 describe 一下它的內容:
1 | |
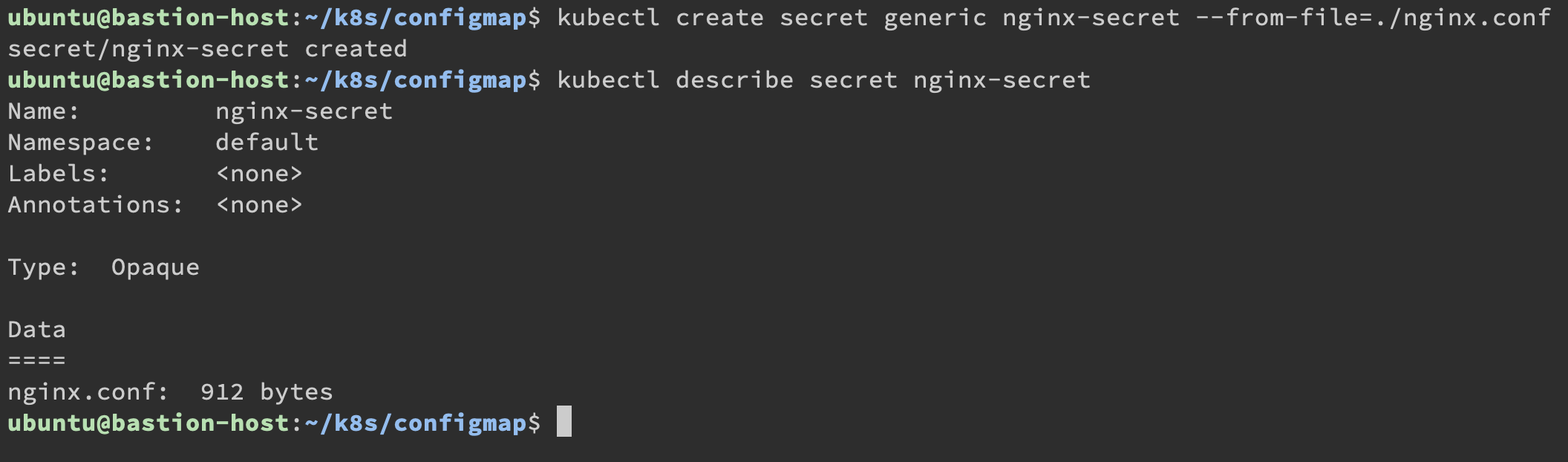
因為是 Secret,他不會直接顯示內容,但可以透過 Edit 方式去編輯,不過在這之前我先來介紹另一個使用情境 kubernetes.io/tls。
kubernetes.io/tls 使用的方式如下:
1 | |
需要注意的是 TLS Key 他只有吃兩個檔案,letsencrypt 的 certbot 會有四個檔案:
cert.pem:本伺服器的公鑰chain.pem:中繼憑證fullchain.pem:中繼憑證 + 本伺服器的公鑰,也就是完整的驗證公鑰privkey.pem:本伺服器的私鑰
在這裡公鑰跟私鑰只需要擺上 fullchain.pem 跟 privkey.pem 即可,公鑰如果擺上 cert.pem 會造成驗證一半的問題,瀏覽器可能會是好的,但 curl 可能結果會是驗證錯誤喔!
雖然看似 Secret 機密,但其實你只要嘗試編輯看看:
1 | |
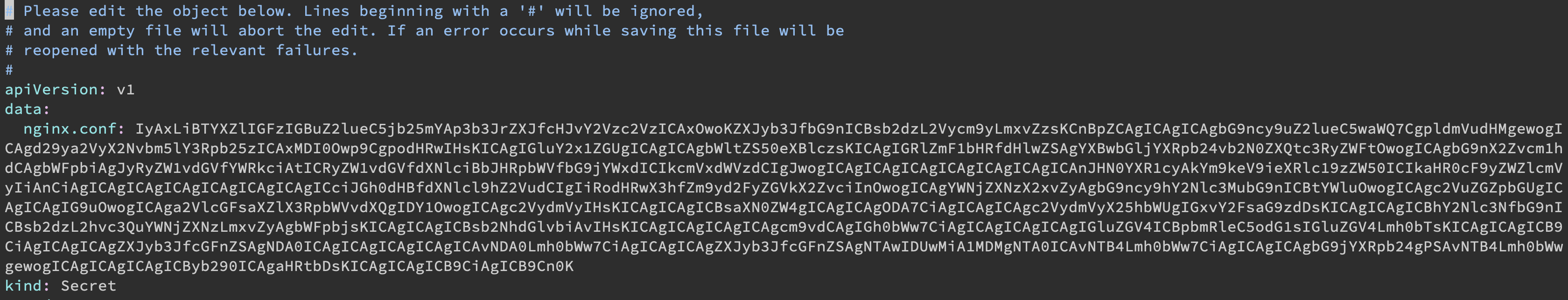
如果對內容覺得很眼熟,你的直覺沒猜錯,它使用的是 Base64 編碼,並不是加密,只要有 K8s 的 etcd 權限也是可以看的到。
想要讓你的資料真的連 etcd 都看不到,也可以嘗試啟用靜態加密,連結我就給在這裡,有需要的可以啟用它去閱讀。
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/encrypt-data/
記得把 nginx-secret 刪除掉:
1 | |
下一篇我們就要來嘗試用這幾天所教的 K8s 來架設跟測試服務啦!
本系列內容也會同步貼到我的 iT 邦幫忙 https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/users/20112934 歡迎來點一下追蹤,那我們就下一篇文章見啦!
Source
- https://www.hwchiu.com/kubernetes-storage-ii.html
- https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10193550
- https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-pod-configmap/
- https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/secret/
- https://blog.miniasp.com/post/2021/02/11/Create-SSL-TLS-certificates-from-LetsEncrypt-using-Certbot
